New (~2028년) IB Physics HL: Full Set
최승호 선생님의 IB Physics
커리큘럼
-
무료 수업 24:53
-
0.1.2 Significant figures25:50
-
0.1.3 Uncertainties27:46
-
0.1.4 Combination of Uncertainties29:04
-
0.1.5 Application on Combination of Uncertainties18:31
-
0.1.6 Graphing and The line of best fit25:47
-
0.1.7 Vector and Scalars20:15
-
0.1.8 Component of vectors | Calculation07:47
-
0.1.9 Vertical and horizontal component of vector30:24
-
무료 수업 49:18
-
A.1.2 Graph for Position and Time18:01
-
A.1.3 Graph for Velocity and Time25:14
-
A.1.4 Acceleration33:54
-
A.1.5 Graph for overall motion27:49
-
A.1.6 SUVAT18:15
-
A.1.7 Projectile motion30:00
-
A.1.8 AIr and fluid resistance10:37
-
A.2.1 Type of forces and Newton's 1st and 2nd law.42:42
-
A.2.2 Newton's 3rd law and Friction35:59
-
A.2.3 Advanced forces I: Elevator and Inclined Planes53:08
-
A.2.4 Advanced forces II: Stacked objects26:08
-
A.2.5 Advanced forces III: Pulley and Tension of Rope19:27
-
A.2.6 Mechanics Momentum29:19
-
A.2.7 Mechanics Impluse31:27
-
A.2.8 Centripetal force26:29
-
A.2.9 Centripetal force Pattern I Vertical Path28:34
-
A.2.10 Centripetal force Pattern | Horizontal path I28:44
-
A.2.11 Centripetal force Pattern | Horizontal path II14:52
-
A.2.12 Centripetal force Pattern | Horizontal path III17:44
-
A.3.1 Work30:27
-
A.3.2 Kinetic energy and Potential energy29:07
-
A.3.3 Elastic Potential Energy and Conservation Law26:56
-
A.3.4 Conservation Law Application I48:39
-
A.3.5 Conservation Law Application II29:10
-
A.3.6 Power and Efficiency24:04
-
A.3.7 Energy and power generation - Sankey diagram36:05
-
A.4.1 Rotational equations of motions and graphs23:40
-
A.4.2 Torque05:39
-
A.4.3 Rotational and translational equilibrium14:51
-
A.4.4 Moment of inertia13:18
-
A.4.5 Rotational dynamics and angular momentum15:06
-
A.4.6 Solving rotational problems28:24
-
A.5.1 Galilean transformation19:25
-
A.5.2 Special relativity and time dilation22:59
-
A.5.3 Length contraction12:37
-
A.5.4 Lorentz transformation and velocity addition21:18
-
A.5.5 The muon decay experiment14:19
-
A.5.6 Spacetime interval10:02
-
A.5.7 Spacetime diagrams I11:30
-
A.5.8 Spacetime diagram II11:34
-
무료 수업 48:51
-
B.1.2 Thermal Physics Thermal Concepts II23:37
-
B.1.3 Properties and Stefan Boltzmann Law26:35
-
B.1.4 Wien's Displacement Law and Power26:29
-
B.2.1 Temperature of the Earth43:35
-
B.2.2 The greenhouse effect and global warming28:47
-
B.3.1 Thermal Physics Modelling a gas Macro I23:45
-
B.3.2 Thermal Physics Modelling a gas Macro II46:33
-
B.3.3 Thermal Physics Modelling a gas Micro24:08
-
B.4.1 Thermodynamic concepts and the first law of thermodynamics14:55
-
B.4.2 Isovolumetric isobaric, isothermal and adiabatic processes19:30
-
B.4.3 Second law of thermodynamics and entropy22:10
-
B.4.4 Heat engines, pumps and Carnot cycle18:48
-
B.4.5 Further Carnot cycle problems18:46
-
무료 수업 31:55
-
C.1.2 Graph for Oscillation25:19
-
C.1.3 Phase difference10:12
-
C.1.4 Simple harmonic motion (advanced) (HL)26:08
-
C.1.5 Time period (HL)24:01
-
C.1.6 Energy changes (HL)17:31
-
C.3.1 Intensity and Superposition28:51
-
C.3.2 Polarization29:09
-
C.3.3 Reflection and Refraction34:41
-
C.3.4 Diffraction and Double slit experiment I19:55
-
C.3.5 Double slit experiment II38:08
-
C.3.6 Modulation of two slit interference by one slit diffraction effect (Part 1) (HL)14:59
-
C.3.7 Modulation of two slit interference by one slit diffraction effect (Part 2) (HL)33:09
-
C.3.8 Modulation of two slit interference by one slit diffraction effect (Part 3) (HL)10:34
-
C.3.9 Multiple-slit interference and Diffraction grating (HL)22:08
-
C.4.1 Standing waves38:51
-
C.4.2 Standing waves and Pipe43:43
-
C.4.3 Damping and Resolution10:33
-
무료 수업 24:21
-
D.1/2.2. Orbital motion26:10
-
D.1/2.3 Fields and Forces21:13
-
D.1/2.4 Potential energy and Potential38:30
-
D.1/2.5 Field lines and Equipotential surfaces25:40
-
D.1/2.6 Work done | Gravitational29:31
-
D.1/2.7 Work done | Electric28:05
-
D.3.1 Magnetic field13:37
-
D.3.2 Direction of magnetic force17:40
-
D.3.3 Direction of magnetic force between two wires25:25
-
D.3.4 Magnitude of magnetic force21:47
-
D.3.5 Magnetic force and circular motion20:51
-
무료 수업 29:52
-
E.1.2 Emission and absorption spectra17:49
-
E.1.3 Atom and Isotope19:04
-
E.1.4 Rutherford scattering and Nuclear radius (HL)18:12
-
E.1.5 Electron scattering and Nuclear radius (HL)23:58
-
E.1.6 Nuclear radius and Nuclear density (HL)18:28
-
E.2.1 Photoelectric effect36:11
-
E.2.2 Stopping Potential18:02
-
E.2.3 Graph for photoelectric effect18:57
-
E.2.4 Matter waves22:36
-
E.2.5 Matter waves II15:37
-
E.3.1 Radioactivity36:10
-
E.3.2 Half life and Background radiation22:34
-
E.3.3 Mass defect and binding energy30:10
-
E.3.4 Binding energy per nucleon23:33
-
E.3.5 Nuclear energy level and the neutrino (HL)17:19
-
E.3.6 The law of radioactive decay (HL)15:39
-
E.3.7 Activity and Half life (HL)15:37
-
E.3.8 Problem solving for the law of radioactive decay and activity (HL)30:14
설명
최승호 선생님의 2023년 개정되는 NEW IB Physics (HL) 강좌입니다. (SL과 HL 포함)
2023년 가을 학기에 IB를 시작하는 학생들부터 수강하면 되는 강의입니다!
*최승호 선생님의 강좌는 각 단원별 기본 문제풀이도 포함되어 있습니다!
*얼라이언스 에듀의 모든 IB 과목의 HL 과정 강좌는 SL 내용을 포함하고 있습니다!
일시정지 기간: 21일 4회
교재 다운받는 방법:
인강 수강 시에 선생님의 핵심 노하우가 담긴 필기용 교재를 학생분께 PDF로 드립니다.
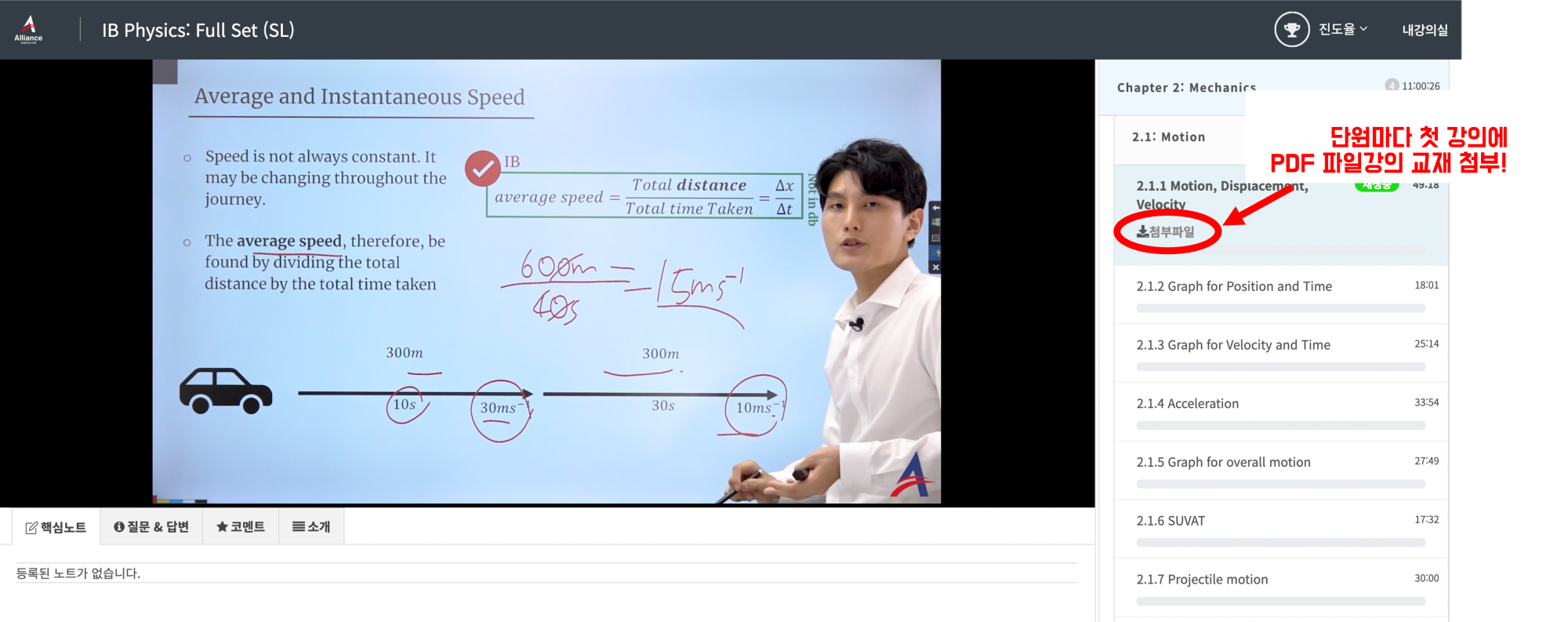
1) 인강 결제 후에 왼쪽 상단에 있는 "내 강의실"에서 구매한 강의를 누르면 아래 사진과 같은 수강 페이지가 보이게 됩니다.
2) 각 단원의 첫 번째 영상을 보면 "첨부파일" 버튼이 있는데, 이를 누르면 PDF가 열려서 다운이 가능합니다^^
질문하기 방법:
인강 수강 시에 강의에서 궁금한 내용을 올리시면 다음날 까지는 답변을 드려요~
선생님의 빠르고 정확한 답변을 위해 학생분들은 아래 형식을 꼭 지켜주세요!
1. 궁금한 부분의 강의 영상 번호 (1.1.1)
2. 강의 영상의 시간
3. 궁금한 내용을 구체적으로!

강사 평점
★★★★★ 4.9
코멘트



