IB Chemistry HL: Part 1, 2, 3 (Full Set)
이재훈 선생님
무엇을 배울까요?
IB Chemistry의 1~11 단원
1. Stoichiometry
2. Atomic Structure
3. Periodicity
4. Bonding
5. Thermodynamics
6. Kinetics
7. Equilibrium
8. Acid & Base
9. Reduction & Oxidation
10. Organic Chemistry
11. Spectral Analysis
커리큘럼
-
1.1.1 Classification of Matter1:11:21
-
1.1.2 Five main types of chemical reactions39:37
-
무료 수업 42:41
-
1.2.1 Mole 1: mole to particles40:12
-
1.2.2 Mole 2: balancing chemical equation23:56
-
1.2.3 Mole 3: mole to mass36:24
-
1.2.4 Mole 4: mole to volume of gas35:28
-
1.2.5 Mole 5: mole to concentration40:06
-
1.2.6 Mole 6: dilution27:11
-
1.2.7 Mole 7: Titration35:35
-
1.2.8 Mole 8: Back Titration33:38
-
1.2.9 Limiting reactant, Excess reactant, Yield36:52
-
1.3.1 Empirical & Molecular formula22:32
-
1.3.2 Determining empirical formula 1: Using mass percentage composition26:54
-
1.3.3 Determining empirical formula 2: Combustion analysis28:05
-
2.1.1 Atomic Structure37:11
-
2.1.2 Isotope48:11
-
2.1.3 History of Atomic models11:07
-
2.2.1 Bohr's model of Hydrogen atom1:17:20
-
2.2.2 Electronic Configuration1:07:50
-
2.2.3 Electronic Configuration Q&A18:47
-
3.1.1 Composition of periodic table43:11
-
3.1.2 Metal and Nonmetal, Melting & Boiling point across period27:56
-
3.2.1 Seven Periodic Trend 1: Effective Nuclear Charge & Shielding Effect46:23
-
3.2.2 Seven Periodic Trend 2: Electronegativity34:33
-
3.2.3 Seven Periodic Trend 3: Atomic & Ionic Radius49:56
-
3.2.4 Seven Periodic Trend 4: Ionization Energy 11:14:29
-
3.2.5 Seven Periodic Trend 4: Ionization Energy 238:00
-
3.2.6 Seven Periodic Trend 5: Electron Affinity, Metallic character, Nonmetallic character31:22
-
3.2.7 Acid-Base Characteristic of Period 3 Oxide & Acid Rain51:42
-
13.1.1 Transition metal core: Physical & Chemical properties of transition metal17:59
-
13.1.2 Transition metal core: Atomic radius of transition metals11:26
-
13.1.3 Transition metal core: Variable oxidation state24:01
-
13.1.4 Chemical property: Metal Complex 134:06
-
13.1.5 Chemical property: Metal Complex 213:24
-
13.1.6 Transition metal: Catalyst21:52
-
4.1.1 Ionic bond 1: Formation and Strength of Ionic Bond1:08:16
-
4.1.2 Ionic bond 2: Structure and Properties of Ionic Compound45:53
-
4.1.3 Ionic bond 3: Naming of Ionic Compound20:21
-
4.3.1 Covalent bond 1: Formation of covalent bond18:44
-
4.3.2 Lewis structure 1: Drawing Lewis structure59:44
-
4.3.3 Lewis structure 2: Resonance structure30:44
-
4.3.4 Covalent bond 2: Dative(coordinate) covalent bond33:16
-
4.3.5 VSEPR Theory (SL)48:28
-
4.3.6 VSEPR Theory (HL)36:56
-
4.3.7 Polarity of covalent Bond & covalent Molecule1:07:16
-
4.3.8 Structure and properties of covalent molecule15:38
-
4.3.9 Giant covalent molecule49:20
-
4.3.10 Nomenclature of covalent molecule12:57
-
4.4.1 London Dispersion Force49:34
-
4.4.2 Dipole-Dipole44:25
-
4.4.3 Hydrogen bond1:17:29
-
4.4.4 Naming Organic Molecules21:09
-
14.1.1 Hybridization of Orbitals37:43
-
14.1.2 Covalent Bond Type: Sigma bond & Pi bond29:31
-
5.1.1 Laws of thermodynamics42:55
-
5.1.2 Definition of enthalpy21:36
-
5.1.3 Endothermic & Exothermic reaction51:00
-
5.2.1 Calorimetry 1: Heat Calculation38:30
-
5.2.2 Calorimetry 2: Enthalpy change of combustion43:02
-
5.2.3 Calorimetry 3: Enthalpy change of neutralization45:47
-
5.3.1 Enthalpy change of formation 1: Definition50:30
-
5.3.2 Enthalpy change of formation 2: Calculation37:13
-
5.4.1 Hess's Law 122:00
-
5.4.2 Hess's Law 238:51
-
5.4.3 Enthalpy change of combustion27:31
-
5.5.1 Bond enthalpy 1: Definition40:11
-
5.5.2 Bond enthalpy 2: Calculation & Source of error52:50
-
5.5.3 Naming Organic Molecules21:09
-
5.5.4 Bond enthalpy 3: Ozone depletion52:09
-
15.1.1 Further types of enthalpies related to ionic compound54:03
-
15.1.2 Born-Haber Cycle 1: Ionic solid to gas42:57
-
15.1.3 Born-Haber Cycle 2: Ionic solid to solution39:14
-
6.1.1 Definition of Reaction Rate1:09:24
-
6.1.2 Techniques for measuring Rates1:11:58
-
16.1.1 Rate Expression 1: Writing rate expression37:47
-
16.1.2 Rate Expression 2: Determining Order of reactant29:59
-
16.1.3 Rate Expression 3: Graphical Representation24:03
-
8.2.1 Arrhenius Acid & Base: Definition17:12
-
8.2.2 Bronsted Lowry Acid & Base 1: Definition30:53
-
8.2.3 Bronsted Lowry Acid & Base 2: Conjugate Acid-Base pair29:06
-
8.2.4 Bronsted Lowry Acid & Base 3: Amphiprotic species & Amphoteric species27:57
-
8.2.5 Lewis Acid & Base 1: Definition28:24
-
8.2.6 Lewis Acid & Base 2: Further application17:13
-
8.3.1 Strong Acid & Base 1: Definition23:29
-
8.3.2 Strong Acid & Base 2: Property of Different Strength25:56
-
8.3.3 Strong Acid & Base 3: Conjugates of Strong & Weak species24:41
-
8.3.4 Hydrolysis of Salt25:11
-
8.4.1 Definition of pH & pOH36:55
-
8.4.2 Auto Ionization of Water34:08
-
8.4.3 Titration Calculation35:35
-
8.4.4 Titration Curve29:05
-
8.4.5 Titration of Strong Acid & Strong Base41:13
-
8.5.1 Anthropogenic formation of acid rain18:41
-
8.5.2 Problems of acid deposition14:23
-
8.5.3 Solution to acid deposition09:42
-
무료 수업 28:46
-
18.1.2 Base dissociation constant (Kb) and pKb14:48
-
18.1.3 Relationship between Conjugates25:20
-
18.1.4 Temperature dependence of Kw39:24
-
18.2.1 Titration of Weak acid - Strong base1:12:52
-
18.2.2 Titration of Strong acid - Weak base30:18
-
9.1.1 Definition of Oxidation & Reduction21:04
-
9.1.2 Oxidation State44:08
-
9.1.3 Balancing Redox Reaction32:51
-
9.2.1 Redox Titration 1: Iron with Permanganate ions16:05
-
9.2.2 Redox Titration 2: Winkler Method20:02
-
19.1.1 Standard Electrode Potential48:57
-
19.1.2 Cell Potential (E)21:04
-
19.1.3 Spontaneity of Cell19:42
-
무료 수업 38:57
-
10.1.2 Nomenclature 2: Identifying Main Functional Group1:13:18
-
10.1.3 Nomenclature 3: Identifying Substituent Group28:47
-
10.2.1 Homologous Series16:05
-
10.2.2 Structural Isomer35:10
-
10.2.3 Classification of Species39:57
-
10.2.4 Types of Reaction, Bond Fission, Movement of electrons18:06
-
10.2.5 Structure of Benzene (Kekule's Structure)34:43
-
10.3.1 Alkane: Free Radical Substitution Reaction54:02
-
10.3.2 Alkene: Addition Reaction51:21
-
10.3.3 Alcohol: Oxidation Reaction51:45
-
10.3.4 Halogenoalkane: Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction19:29
-
10.3.5 Benzene: Electrophilic Substitution Reaction16:52
-
10.3.6 Overall review of functional group chemistry15:58
-
20.1.1 Halogenoalkane 1: Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction1:03:43
-
20.1.2 Halogenoalkane 2: Q&A16:37
-
20.1.3 Halogenoalkane 3: Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction25:37
-
20.1.4 Alkene 1: Electrophilic Addition Reaction23:49
-
20.1.5 Alkene 2: Markovnikov's Rule23:29
-
20.1.6 Benzene: Electrophilic Substitution Reaction34:25
-
20.1.7 Alcohol & Nitrobenzene: Reduction Reaction31:44
-
20.1.8 Overall review of functional group chemistry16:53
설명
이재훈 선생님의 IB Chemistry (HL) 강좌입니다.
다루는 단원은 Chapter 1~11 입니다. (SL과 HL 포함)
*이재훈 선생님의 강좌는 각 단원별 기본 문제풀이도 포함되어 있습니다!
*얼라이언스 에듀의 모든 IB 과목의 HL 과정 강좌는 SL 내용을 포함하고 있습니다!
일시정지 기간: 15일 3회
교재 다운받는 방법:
인강 수강 시에 선생님의 핵심 노하우가 담긴 필기용 교재를 학생분께 PDF로 드립니다.
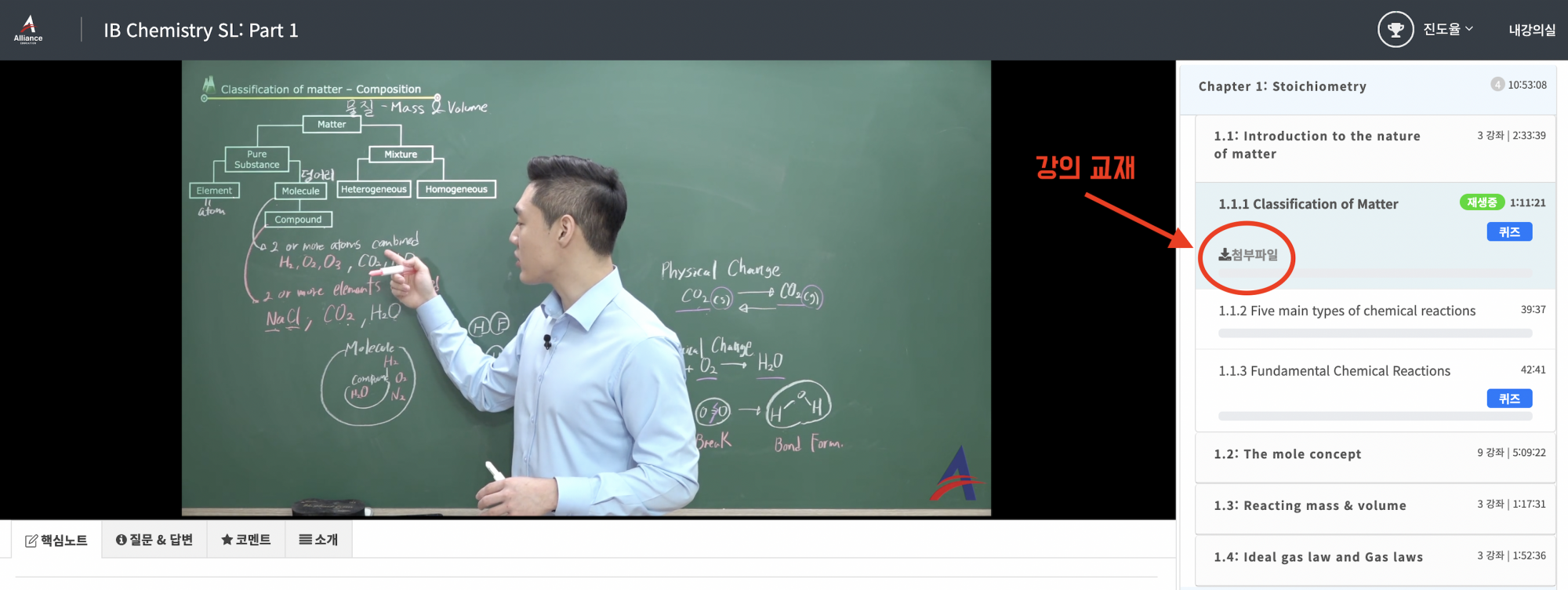
1) 인강 결제 후에 왼쪽 상단에 있는 "내 강의실"에서 구매한 강의를 누르면 아래 사진과 같은 수강 페이지가 보이게 됩니다.
2) 각 단원의 첫 번째 영상을 보면 "첨부파일" 버튼이 있는데, 이를 누르면 PDF가 열려서 다운이 가능합니다^^
질문하기 방법:
인강 수강 시에 강의에서 궁금한 내용을 올리시면 다음날 까지는 답변을 드려요~
선생님의 빠르고 정확한 답변을 위해 학생분들은 아래 형식을 꼭 지켜주세요!
1. 궁금한 부분의 강의 영상 번호 (1.1.1)
2. 강의 영상의 시간
3. 궁금한 내용을 구체적으로!

강사 평점
★★★★★ 5.0
코멘트



